With the rising popularity of ChatGPT, Bard, and other AI chatbots, it can be hard to tell whether a piece of writing was created by a human or AI. There are many AI detection tools available, but the truth is, many of these tools can produce both false-positive and false-negative results in essays, articles, cover letters, and other content. Fortunately, there are still reliable ways to tell whether a piece of writing was generated by ChatGPT or written by a human. This wikiHow article will cover the best AI detection tools for teachers, students, and other curious users, and provide helpful tricks for spotting AI-written content by sight.
Things You Should Know
- Tools like OpenAI’s Text Classifier, GPTZero, and Copyleaks can check writing for ChatGPT, LLaMA, and other AI language model use.
- ChatGPT often produces writing that looks “perfect” on the surface but contains false information.
- Some signs that ChatGPT did the writing: A lack of descriptive language, words like “firstly” and “secondly,” and sentences that look right but don’t make sense.
How AI Detection Tools Work

- AI detection tools evaluate how predictable the text is.ChatGPT, Bard, and similar chatbots “write” content by predicting the next word or sentence based on its training data. Similarly, AI detection tools also work by detecting how predictable the words, sentences, and format are based on similar training data.
- The detection tool compares a piece of writing to similar content, decides how predictable the text is, and labels the text as either human or AI-generated.
- These tools also look for other indicators, or “signatures” that are associated with AI-generated text, such as word choice and patterns.[1]

- AI detectors often make mistakes.ChatGPT detection tools can be helpful, but they aren’t infallible. AI detectors often produce false positive results, meaning that they tend to flag human-written text as AI-generated if it follows certain patterns.[2] It’s also quite easy for students and other writers to modify content written by ChatGPT to make it virtually undetectable by AI detectors, meaning that AI-generated writing could fly under the radar of the detector.
- If an AI detection tool reports that a piece of writing was mostly AI-generated, don’t rely on that report alone. It’s best to only use AI detection tools if you’ve already found other signs that the writing was written by ChatGPT.[3]
- Running a piece of writing through multiple AI detection tools can help you get an idea of how different tools work. It can also help you narrow down false-negatives and false-positives.
Using AI Detection Tools
- OpenAI Text Classifier.This free tool created by the same people who brought us ChatGPT predicts how likely it is that a piece of writing was generated by an AI language model.[4] You’ll need a free OpenAI account to use AI Text Classifier. For now, you can only paste a piece of writing into the tool, but the option to upload documents may be available in the future. Check it out at https://platform.openai.com/ai-text-classifier.
- GPTZero.This AI-detection tool was developed by a student at Princeton University in an effort to combat AI plagiarism.[5] GPTZero gives you the option of pasting or uploading documents to check for ChatGPT and other AI-generated writing, and you can evaluate up to 5000 words per document with the free (Classic) version of the tool. Paid options are available, including a subscription designed for teachers. You can use the tool in your web browser, or by installing the Chrome Extension or Word plugin.[6] Visit https://gptzero.me to create a free account.
- Content at Scale AI Detector.This free online ChatGPT detector was developed by an AI content creation company. Their focus is to help writers who use ChatGPT and other AI content generators edit their work before publishing so it won’t be so obvious that it’s AI written.[7] You can paste 25 words or more into this tool. Try it out at https://contentatscale.ai/ai-content-detector.
- Copyleaks AI Content Detector.If you’re looking for a premium ChatGPT detector that’s secure and equipped to detect content written by GPT-4 (the newest version of OpenAI’s language model that’s only available in ChatGPT Plus), Copyleaks has a variety of subscription plans for checking work for AI plagiarism. Without a paid subscription, you can still evaluate up to 250 characters of writing for ChatGPT, Bard, and other AI chatbot use.[8] Give it a try at https://copyleaks.com/ai-content-detector.
Signs of ChatGPT Use
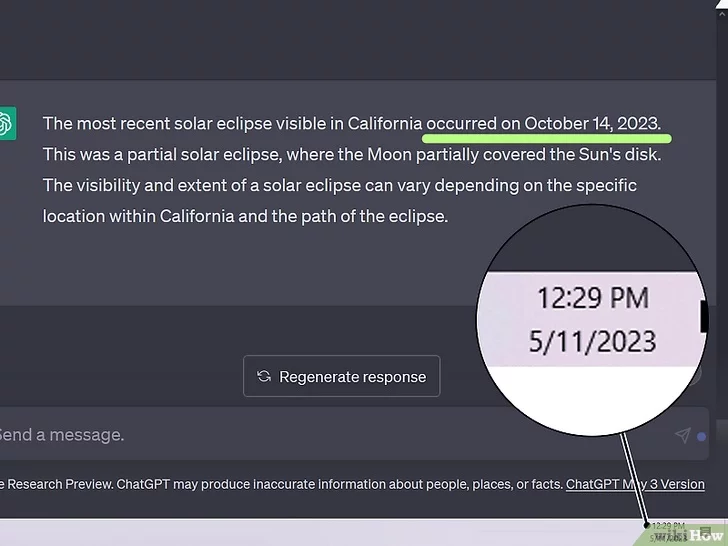
- Implausible or inaccurate statements.ChatGPT, Google Bard, and other generative AI tools are known to hallucinate or make up facts.[9] While students and job applicants can also include inaccuracies in their writing, AI bots make false information seem extremely believable. ChatGPT also has limited knowledge of events that occurred after 2021, which means it usually can’t produce factual information about current events.[10] If the writing seems very well-written but contains false information, it could be AI generated.
- If you’re evaluating a piece of writing for potential AI use, try searching the web for a few facts from the text. Try to search for facts that are easy to verify—e.g., dates and specific events.
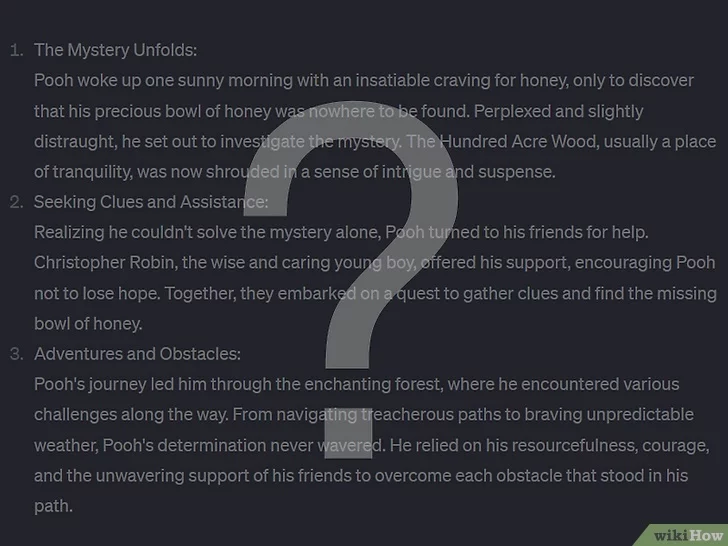
- Some sentences look right, but don’t actually make sense.ChatGPT can create grammatically perfect sentences that don’t make sense, even though they look great on the surface. This is because ChatGPT doesn’t know whether something is true or false—it only knows how to use the right kind of word in the right place. If you find yourself rereading something that looks like it should make sense, but you can’t grasp what the sentence is trying to say, there’s a good chance you’re looking at AI-generated writing.

- Uses words like “firstly,” “secondly,” “therefore,” and “in conclusion.”While many school-age essay writers also use this type of language when laying out their essays, you’ll almost always see these words in ChatGPT-written essays. Some AI detection tools will even flag human-written content as AI-written because it includes these terms.
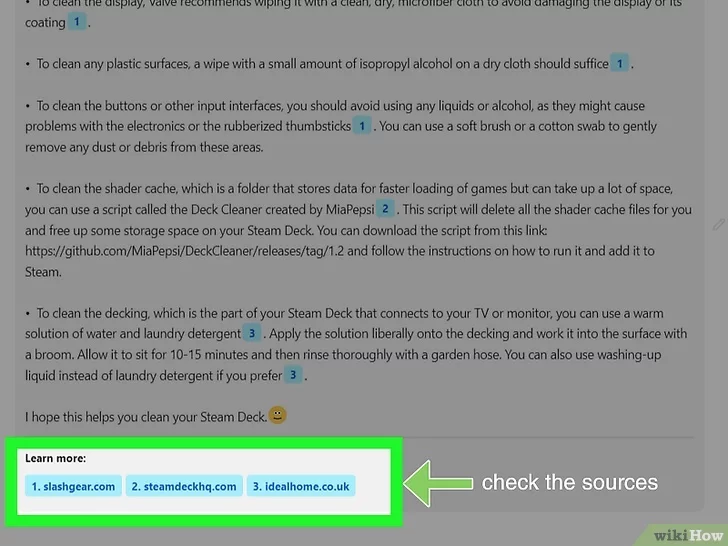
- Fake or inaccessible sources.While the version of ChatGPT that’s built into Bing cites sources automatically, the standard version of ChatGPT tends to make up sources that don’t exist.[11] If you’re a teacher evaluating a student essay or a student who uses ChatGPT to find sources, double-check the sources provided by ChatGPT to make sure they’re real.
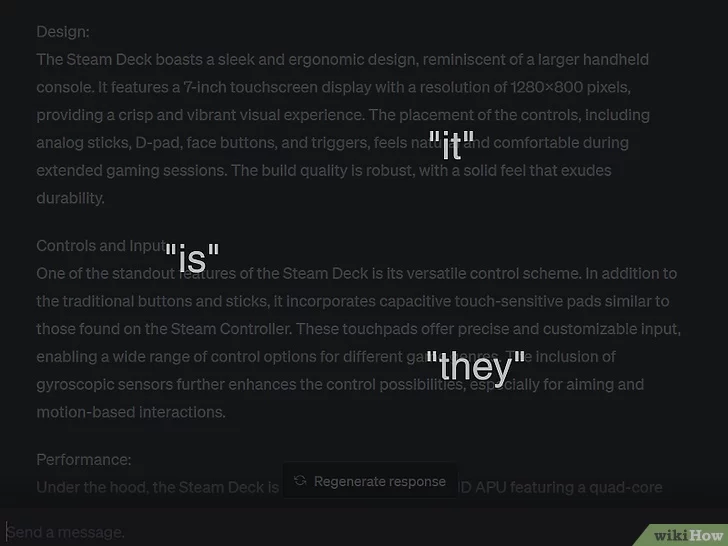
- A lack of descriptive and “rare” words.AI models like ChatGPT work by predicting the next word in a sentence, which results in lots of non-specific words like “it,” “is,” and “they.” Because ChatGPT is less likely to use rarer words to describe things, an overall lack of descriptive language could mean that ChatGPT wrote the content.[12]

- No grammatical or spelling errors.While students, job applicants, and authors do their best to catch all grammatical and spelling errors before turning in their writing, it’s hard to catch everything. Computers, on the other hand, produce grammatically impeccable work—even if it the writing isn’t factual.
- When in doubt, ask ChatGPT to produce a similar piece of writing.If you think ChatGPT wrote an essay, letter, or other bit of text, log in to ChatGPT and ask the chatbot to create similar content using the writing’s main points. If ChatGPT’s response contains the same structure as the piece of content you’re evaluating, it’s possible the writer used ChatGPT.
- For example, if you’re evaluating a cover letter for AI use, you might tell ChatGPT, “Write me a cover letter for a junior developer position at Company X. Explain that I graduated from Rutgers with a Computer Science degree, love JavaScript and Ruby, and have been working as a barista for the past year.”
- Because ChatGPT is conversational, you can continue providing more context. For example, “add something to the cover letter about not jumping right into the industry after college because of the pandemic.”
Tips
- Cornell researchers determined that humans incorrectly found AI-generated news articles credible more than 60% of the time.[13]
- If you’re using a ChatGPT detection tool that identified writing as AI-written, consider that it may be a false positive before approaching the situation with the writer.
- If you suspect ChatGPT wrote something but can’t tell for sure, have a conversation with the writer. Don’t accuse them of using ChatGPT—instead, ask them more questions about the writing or content to make their knowledge lines up with the content. You may also want to ask them about their writing process to see if they admit to using ChatGPT or other AI writing tools.
References
- ↑https://www.turnitin.com/blog/ai-writing-the-challenge-and-opportunity-in-front-of-education-now
- ↑https://www.turnitin.com/blog/understanding-false-positives-within-our-ai-writing-detection-capabilities
- ↑https://platform.openai.com/docs/chatgpt-education
- ↑https://platform.openai.com/ai-text-classifier
- ↑https://www.npr.org/2023/01/09/1147549845/gptzero-ai-chatgpt-edward-tian-plagiarism
- ↑https://app.gptzero.me/app/subscription-plans
- ↑https://contentatscale.ai/ai-content-detector/
- ↑https://copyleaks.com/api-pricing
- ↑https://research.google/pubs/pub51844/
- ↑https://help.openai.com/en/articles/6783457-what-is-chatgpt
- ↑https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9939079/
- ↑https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/12/19/1065596/how-to-spot-ai-generated-text/
- ↑https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/12/19/1065596/how-to-spot-ai-generated-text/
ADVERTISEMENT
